The Afirma Team
August 8, 2025
Veracyte recently returned from the American Association of Clinical Endocrinology (AACE) Annual Meeting in Orlando and the 17th Annual International Thyroid Congress (ITC), where we were happy to contribute our first 3 posters of the year.
American Association of Clinical Endocrinology (AACE) Annual Meeting 2025
At AACE, we presented an abstract in which the authors assessed the impact of pre-operative detection of PLEKHS1 promoter mutations in thyroid nodules:
Analysis of Pleckstrin Homology Domain Containing S1 (PLEKHS1) Promoter Mutations in Pre-Operative Thyroid Nodule Samples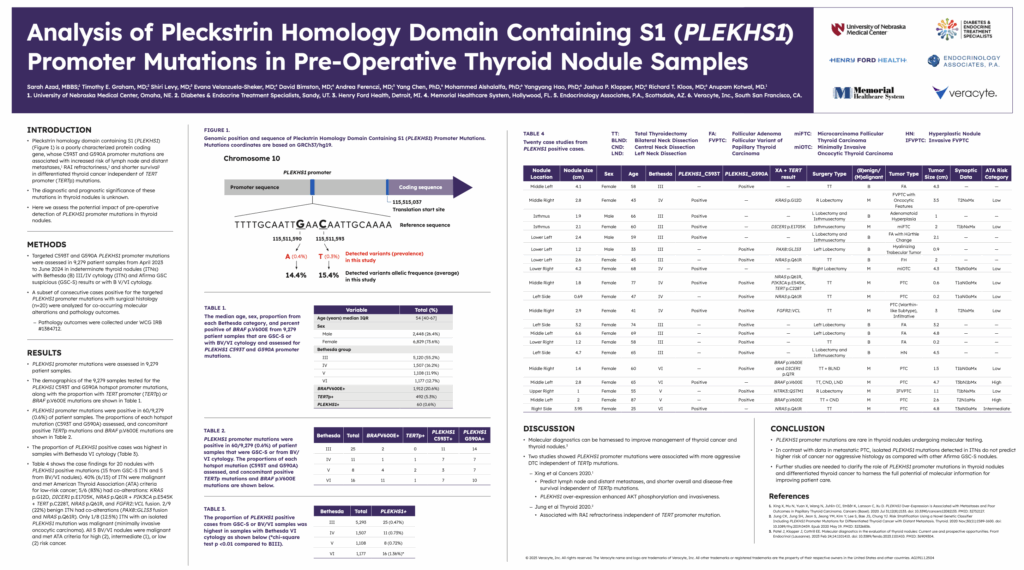
PLEKHS1 is a poorly characterized gene located on chromosome 10 that encodes the protein Pleckstrin homology domain containing S1. Mutations at the C593T and G590 hotspots in the promoter region are associated with more aggressive thyroid tumor behavior in differentiated thyroid cancer independent of TERT promoter (TERTp) mutations.1,2
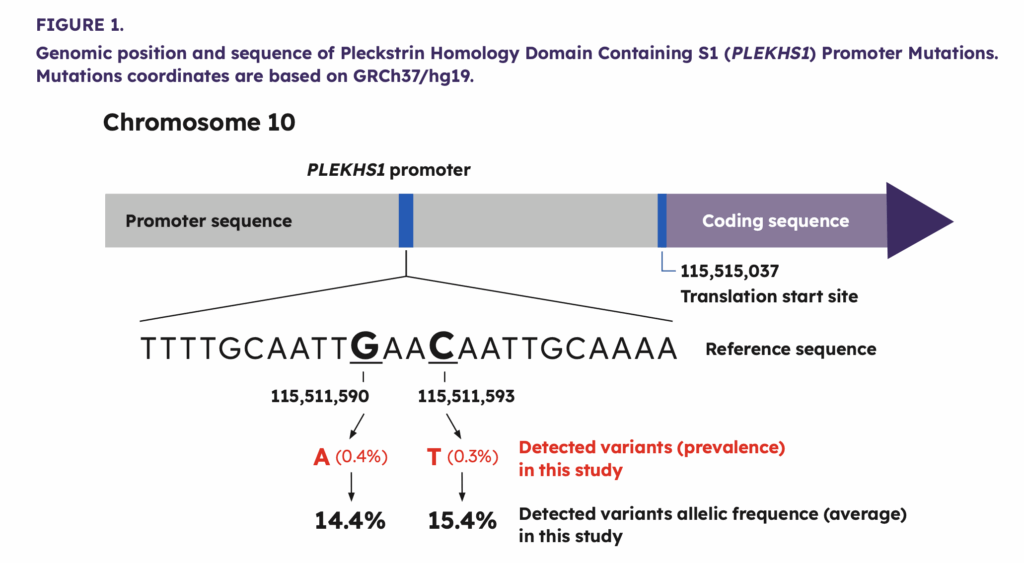
More specifically, Xing et al demonstrated an increased risk of lymph node metastases, distant metastases, and shorter survival, and Jung et al demonstrated RAI refractoriness. However, it was recognized that additional studies are needed to fully understand the diagnostic and prognostic utility of detecting PLEKHS1 promoter mutations in indeterminate thyroid nodules (ITN).1,2
This study aimed to contribute to the greater understanding of this topic by analyzing a large cohort of patient samples and reporting on prevalence, Bethesda category, co-occurring mutations, and surgical outcomes (among a subset of 20 samples).
The cohort consisted of 9,279 patient samples collected between April 2023 and June 2024 with either Bethesda V/VI cytology, or Bethesda III/IV cytology and an Afirma GSC Suspicious result.
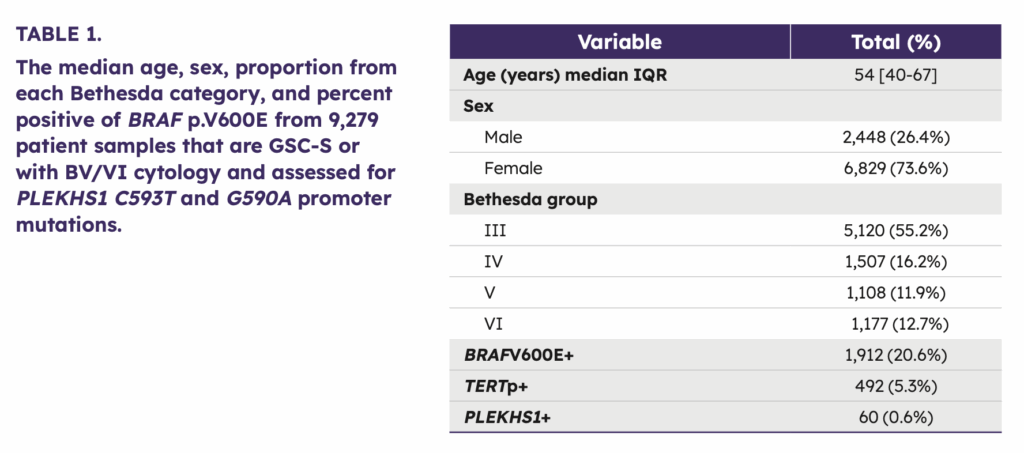
Out of this cohort, 60 were found to be positive for PLEKHS1 C593T or G590A hotspot promoter mutations for a prevalence of 0.6%. Of these 60 samples, a subset of 20 samples with surgical histology were analyzed for pathology outcomes and co-occurring molecular alterations.
Ultimately, this study found that in contrast to metastatic PTC, isolated PLEKHS1 mutations found in indeterminate thyroid nodules do not correlate with a higher ROM or more aggressive disease, though further studies are needed to fully understand the role that PLEKHS1 mutations play in thyroid disease.
The 17th International Thyroid Congress (ITC)
We also had the privilege of contributing the following 2 scientific abstracts to the International Thyroid Congress in Rio De Janeiro:
The Genomic Landscape of 250,000+ Thyroid Nodules Undergoing Exome-Enriched RNA Sequencing
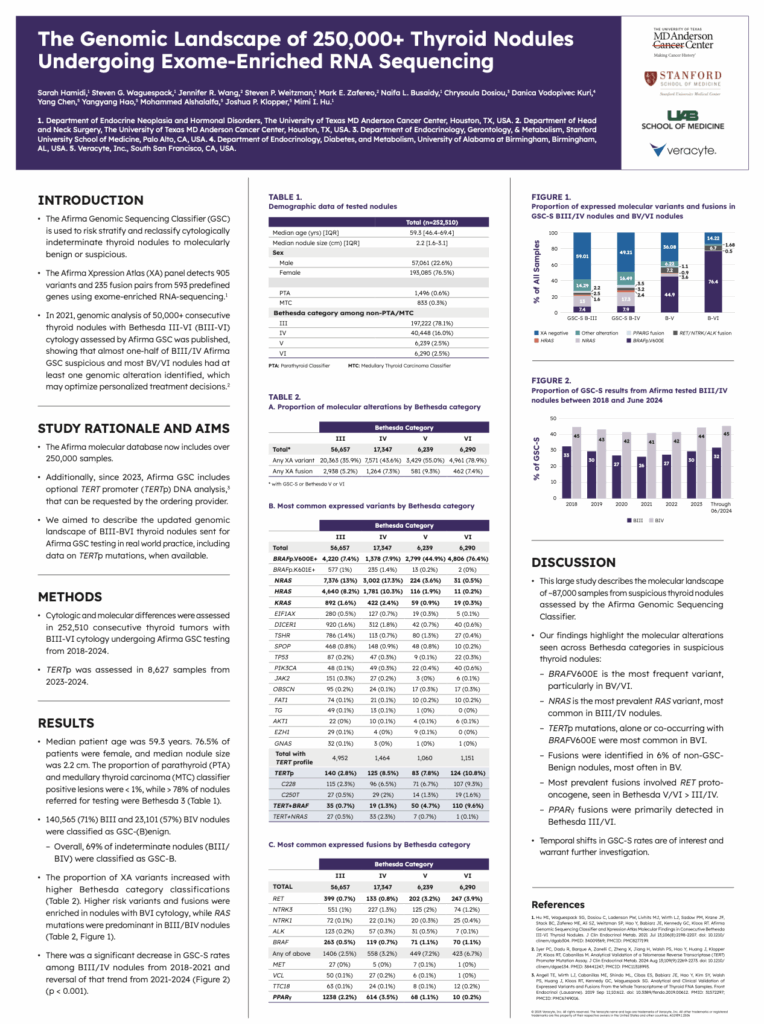
The first poster, The Genomic Landscape of 250,000 Thyroid Nodules Undergoing Exome-enriched RNA Sequencing, is an expansion of Hu et al JCEM 2021, an analysis of over 50,000 BIII-VI nodules assessed by Afirma GSC.3 This poster aimed to describe the updated genomic landscape of over 250,000 BIII-BVI thyroid nodules sent for Afirma GSC testing in real world practice, with the addition of data on TERTp mutations.4
252,510 consecutive thyroid tumors with BIII-VI cytology undergoing Afirma GSC testing from 2018-2024 were assessed for cytologic and molecular differences. Out of these samples, TERT DNA analysis was performed in 8,627 samples from 2023-2024.
In this study, the researchers reported on demographic data and molecular alteration data, reporting findings such as:
The Genomic Landscape of Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma Identified by the Afirma RNA-Sequencing Classifier: Insights from a Large Real-World Cohort
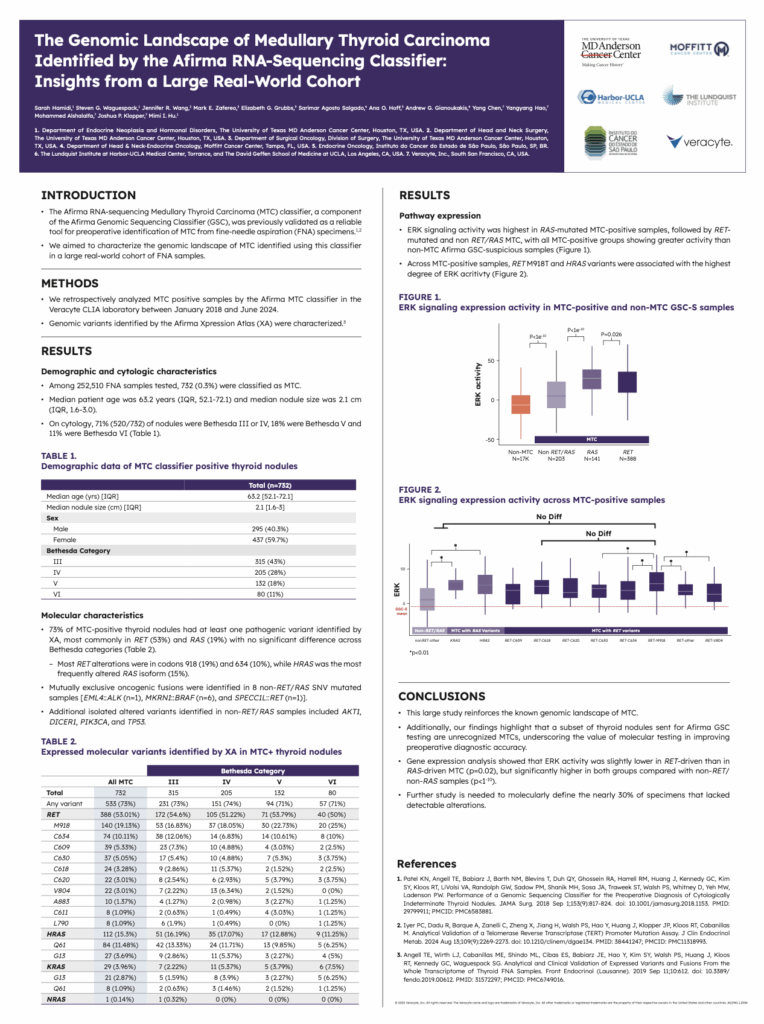
The second poster, titled The Genomic Landscape of Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma (MTC) Identified by the Afirma RNA-Sequencing Classifier: Insights from a Large Real-World Cohort, retrospectively analyzed MTC positive samples by the previously validated Afirma MTC classifier in the Veracyte CLIA laboratory between January 2018 and June 2024.5
This study aimed to characterize the genomic landscape of MTC identified using the MTC classifier component of Afirma GSC in a large real-world cohort of FNA samples. Using this cohort of MTC positive samples analyzed in the Veracyte CLIA laboratory between January 2018 and June 2024, the poster reported demographic, cytologic, molecular, and pathway expression data, such as:
Demographic and cytologic characteristics
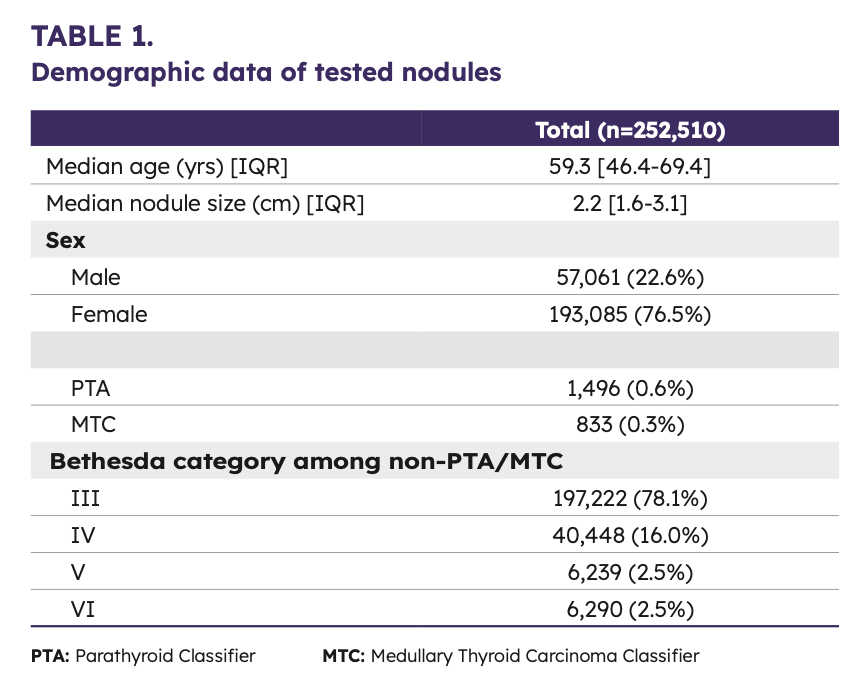
Molecular characteristics
Pathway expression
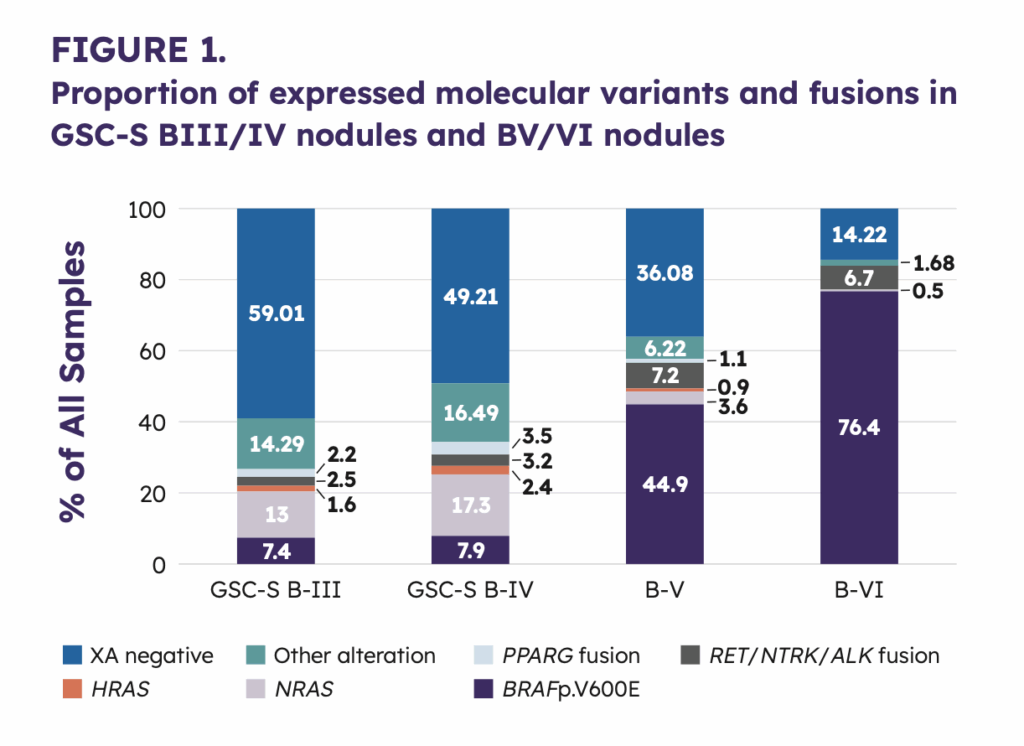
Gene expression analysis revealed that ERK signaling activity was highest in RET mutated MTC-positive samples, followed by RET-wildtype MTC-Positive samples, with both groups showing greater activity than non-MTC Afirma GSC-suspicious samples.
Across MTC-positive samples, RET M918T and HRAS variants were associated with the highest degree of ERK activity.
Ultimately, the study reinforced the known genomic landscape of MTC, but further study is needed to molecularly define the nearly 30% of specimens lacking detectable alterations.
Conclusion
We’re happy that Veracyte could contribute to the 2025 AACE and ITC annual meetings by presenting research made possible by Afirma GSC and GRID (Genomic Resource for Intelligent Discovery).
References